Blog
Difference between Intensive and SelectiveDistribution in Marketing
Difference between Intensive and Selective Distribution in Marketing
Generally speaking, Marketing is considered a process that entices people to sell and buy things, but it does not limit here. It encompasses other marketing nuances such as product promotion, designing, distribution, and creating online content for social media in a broader sense. In any business, the concept of marketing determines customer satisfaction and trust. Through marketing, the manufacturer promotes his product and increases sales.
There are different types of marketing- digital and offline. Whichever be the preference, the business's success lies in the strategic approach of marketing and sale. There are four fundamental Ps of marketing-
> Product
Price
The four fundamental Ps of marketing are consistent aspects to acknowledge while having a strategic approach in marketing. These four Ps may have developed their ways and patterns due to digitization, but they remain the marketing strategy basics. It is the Placement channel that has been evolved over a period of time by comprising more resources from digital services.
What is Distribution?

Distribution in Marketing means delivering and selling products from manufacturers to potential customers. In other words, it means how efficient marketing is to make the services and products available for people. In the process of Distribution, companies also try to gather information from the consumers that can be used for identifying key improvements and opportunities for the growth of business in the market.
In a good Distribution technique, there should be limited stops for the product to reach the customers; the means of distribution, i.e.-transportation, and legalities should be used effectively.
Who is a Distributor?
A Distributor is a medium between the manufacturer and the customer. He is the one who buys products from the manufacturer and sells them to the customer. The success of the business lies with the skillful distribution management by the distributor.
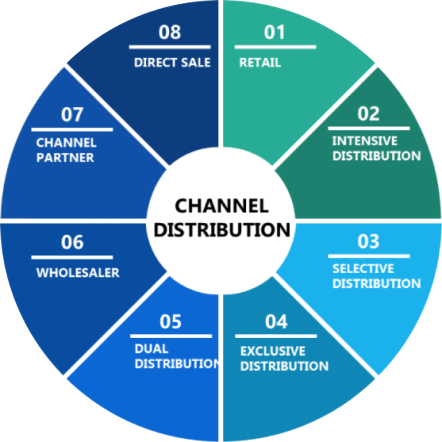
Channels of Distribution
In marketing, the distribution works in two ways- The indirect channel has direct contact with the distributor. In the indirect channel, the mediators (distributors) work to make a connection.
Distribution channel stands for the journey of the business that starts from manufacturer to the customer; there are eight types of distribution channels-
What is Intensive Distribution
This distribution channel works best for generic products where different possible sources are used for distribution so that the products are readily available to customers. In this distribution strategy, the manufacturing processes to sell its products and services in many retail outlets in the same area. The customers can buy the product on the spot without going around and taking pain to find one. These are mass-products present in people's everyday lives, like newspapers, magazines, soft drinks, water bottles, cigarettes, etc., fall in this category. The e-marketing examples are Amazon, eBay where producers can sell their products in online markets.
The most important factor in this channel is that the manufacturer has to produce a massive amount of products to provide enough supply in the target geographical area. The level of distribution the producer chooses depends upon the production capacity, target market, pricing, and promotion policies. This distribution technique is helpful for the products that have no particular market segment as they are bought by almost everyone.

Advantages of Intensive distribution
01. Analyze the market
The company and the producer have the opportunity to analyze the source of sale whether the product is in more demand in local vendors or supermarkets. The company can analyze the data and figure out how to increase the sale and presence of the product in the market.
02. Awareness of the product
With the promotion of the products in many places, local shops, and superstores, the customer relates the information already seen in the ads to become aware of the product.
03. Large scale sale and profit
In this strategy, the company has many retailers and distributors, which increases product sales. The company can make a large profit as more products are sold due to their availability in many places.The business model of a company will be dictating whether upselling or cross-selling is more lucrative. For instance, in a typical e-commerce business where a high fixed cost is added to orders by shipping or customer acquisition, companies will usually intend to increase the average order value to minimize the effect of these expenses.
04. The benefit of alternate selection
Customers have the choice to buy another product from the shelf when one brand is not available. He doesn’t need to go to another store as there are other options available.
05. Maintaining trust
Another advantage is building trust. As the customer sees the product in many places, many stores, and local shops, he starts believing in the authenticity and quality of the product.
Disadvantages of Intensive Distribution
01. Expenses in Distribution
Since FMCG products are usually in huge demand, they are the products of day-to-day use, with the resulting company having to produce them in bulk to make them available to different distributors. Still, sometimes they all don't get sold out, but the cost of production has to be borne by the producers.
02. Managing business partners
In intensive distribution, there are a large number of distributors and retailers involved in the business, which is challenging to manage. The stores and retailers may be located in different places. Therefore the company may require more people for outreaching that could cause extra expenses.
03. Low pricing model
There is very high competition in product price when a large number of products are available in the market. It is not wise on the manufacturer's part to raise the product's price as the customer readily can switch to another product if the price of one product is not favorable.
04. Managing mediators
Intensive distribution works across different channels, which needs to be managed by a mediator or an agent. Although the need for an agent can not be denied in profitable negotiations, the risk of making appropriate decisions is always there. The company has to have trust in their negotiations.
What is Selective Distribution
What is Selective Distribution
One important fact about Selective distribution is that if the store is much visited and popular, it will be beneficial for the producer. The Selective distribution agreement restricts the distributors to sell the product to limited distributors or the customers. High-end products as- cars, tv, expensive clothes, etc., come under this category.

